We should avoid the term “fluid overload”, Critical Care
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 03 julho 2024
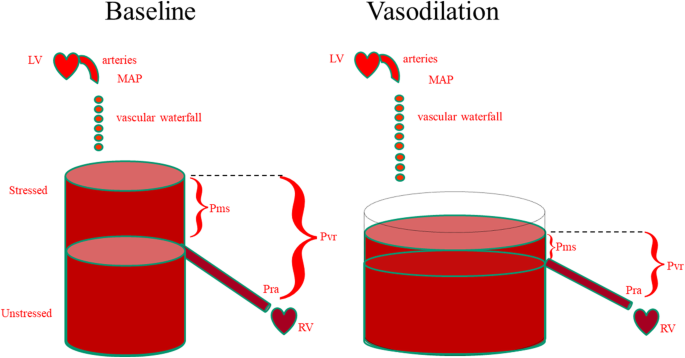

Hypovolemia: What Is It, Causes, Signs, and More
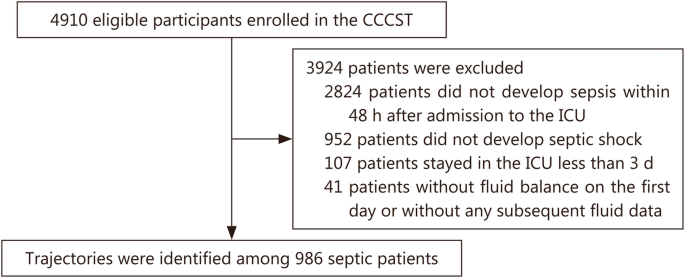
Association of fluid balance trajectories with clinical outcomes in patients with septic shock: a prospective multicenter cohort study, Military Medical Research
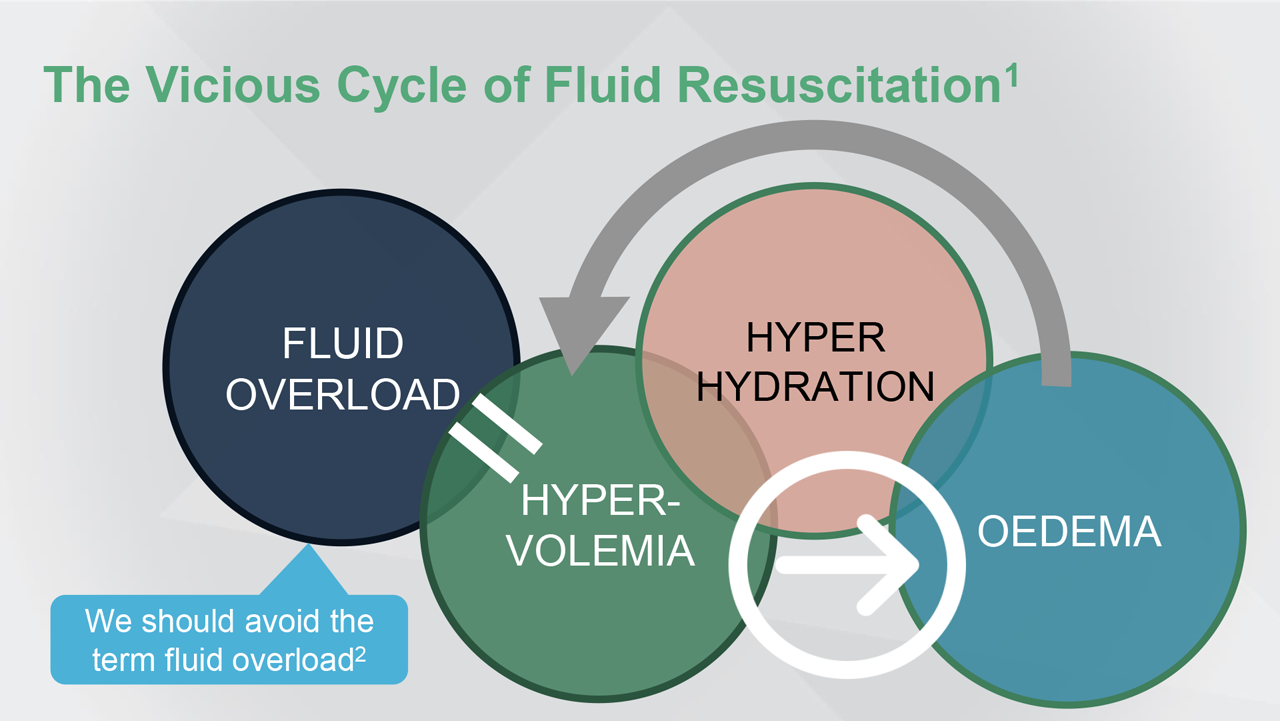
Optimising Fluid Therapy in the Critically Ill - The International Fluid Academy

Fluid Volume Overload and Congestion in Heart Failure

Sympathetic Crashing Acute Pulmonary Edema (SCAPE) - EMCrit Project

Organ Systems and Related Effects of Fluid Overload. 5-12 Organ System
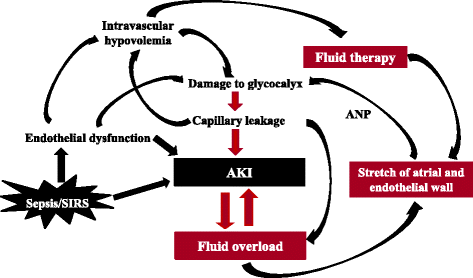
Fluid overload and acute kidney injury: cause or consequence?, Critical Care

Extracorporeal Ultrafiltration for Fluid Overload in Heart Failure: Current Status and Prospects for Further Research - ScienceDirect
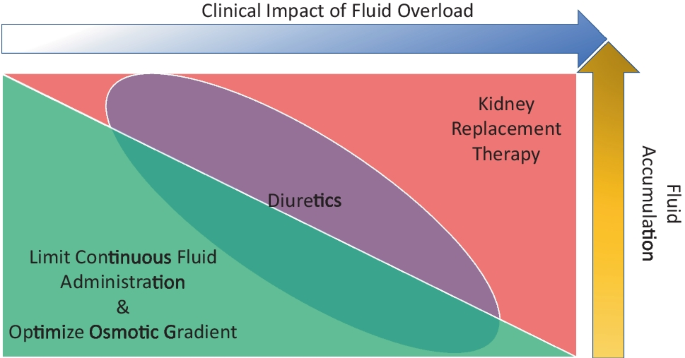
Fluid assessment, fluid balance, and fluid overload in sick children: a report from the Pediatric Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) conference
Recomendado para você
-
What is the meaning of I'm overloaded ? - Question about03 julho 2024
-
Sohee Fit - Progressive overload, simply defined, refers03 julho 2024
-
S3 Fitness Studio - ⭕️ What is PROGRESSIVE OVERLOAD03 julho 2024
-
What is Java method overloading? - Quora03 julho 2024
-
Overloaded - Definition, Meaning & Synonyms03 julho 2024
-
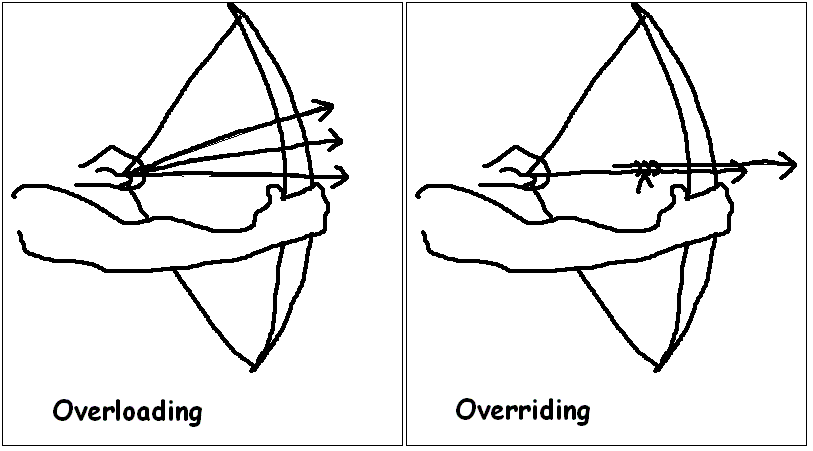 Possibilities for function overloading in compile-to-JS languages03 julho 2024
Possibilities for function overloading in compile-to-JS languages03 julho 2024 -
 Meaning to Read: Cognitive Overload Resulting From Lack of Oral03 julho 2024
Meaning to Read: Cognitive Overload Resulting From Lack of Oral03 julho 2024 -
 Cuteness overloaded😘😘 Actor photo, Cute actors, Telugu hero03 julho 2024
Cuteness overloaded😘😘 Actor photo, Cute actors, Telugu hero03 julho 2024 -
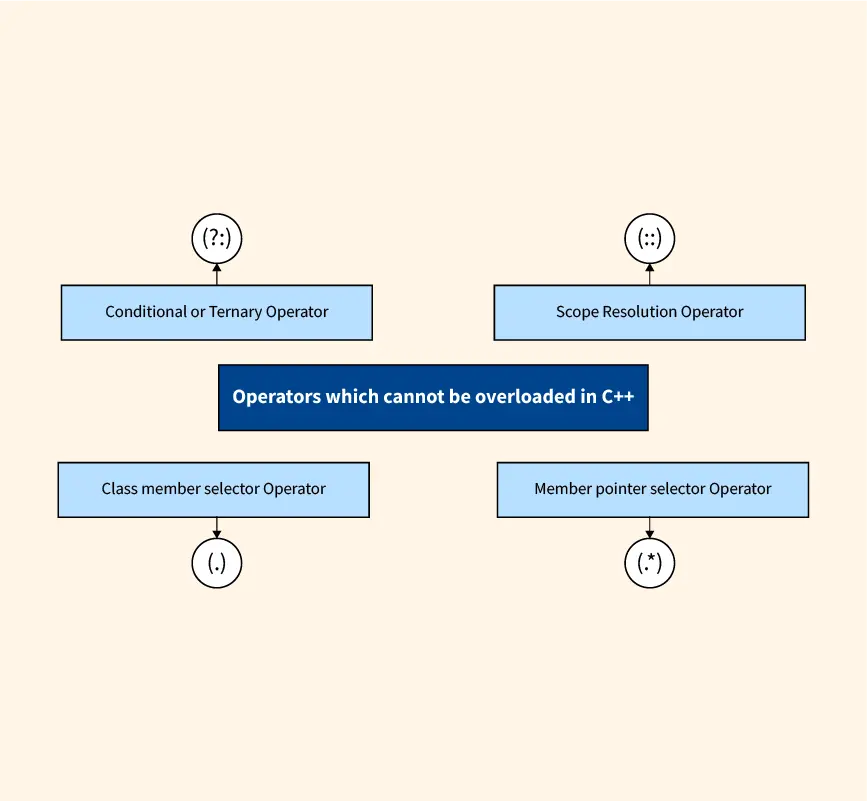 Which Operator Cannot Be Overloaded in C++?03 julho 2024
Which Operator Cannot Be Overloaded in C++?03 julho 2024 -
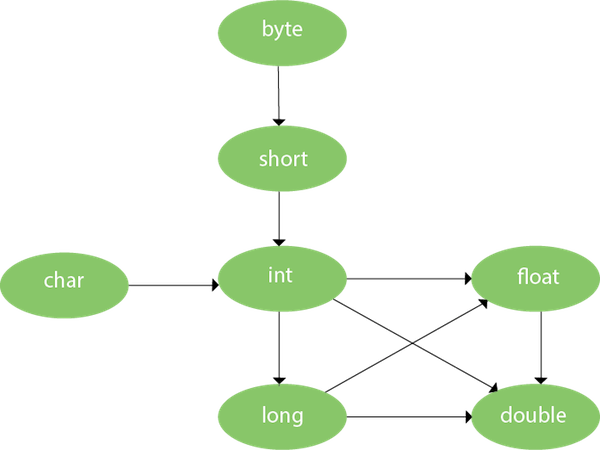 Method Overloading in Java - Javatpoint03 julho 2024
Method Overloading in Java - Javatpoint03 julho 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Girl Neón Gacha Life* Neon, Neon cat, Cat girl03 julho 2024
Girl Neón Gacha Life* Neon, Neon cat, Cat girl03 julho 2024 -
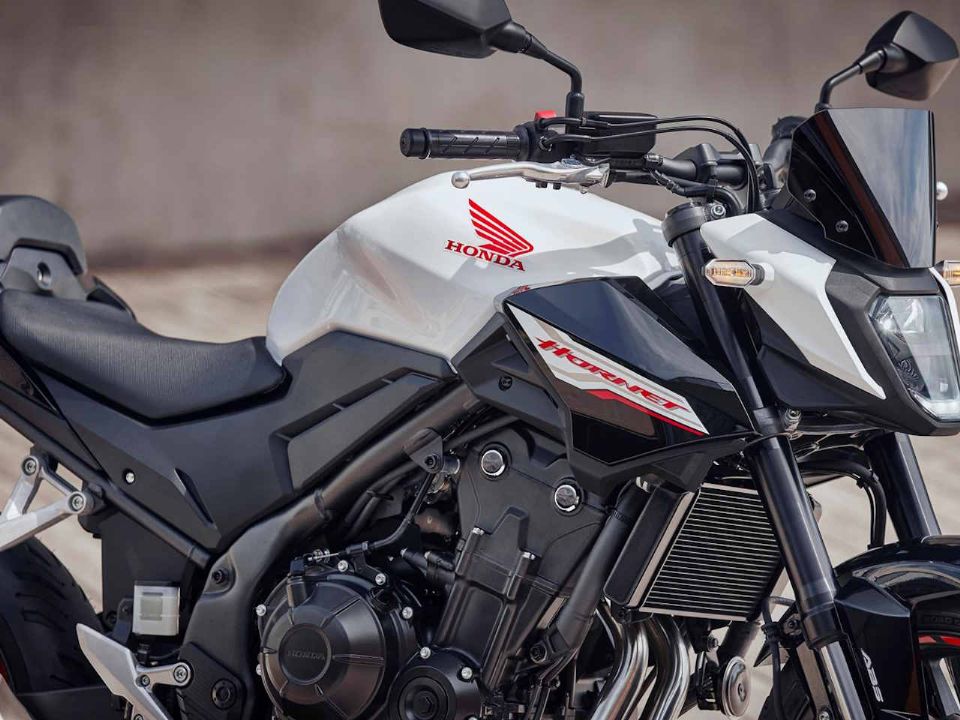 Honda Hornet 500: a sucessora da CB 500F - MOTOO03 julho 2024
Honda Hornet 500: a sucessora da CB 500F - MOTOO03 julho 2024 -
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/41954278/sanstitrebietc.0.0.png) PSA: You can now purchase and pre-order Nintendo eShop games on the web - Polygon03 julho 2024
PSA: You can now purchase and pre-order Nintendo eShop games on the web - Polygon03 julho 2024 -
 RedeCanais Novo Endereço: bit.ly/redecanais10 - Assistir Animes03 julho 2024
RedeCanais Novo Endereço: bit.ly/redecanais10 - Assistir Animes03 julho 2024 -
 ICE SCREAM 4 Full Gameplay - Android Horror Neighborhood Game03 julho 2024
ICE SCREAM 4 Full Gameplay - Android Horror Neighborhood Game03 julho 2024 -
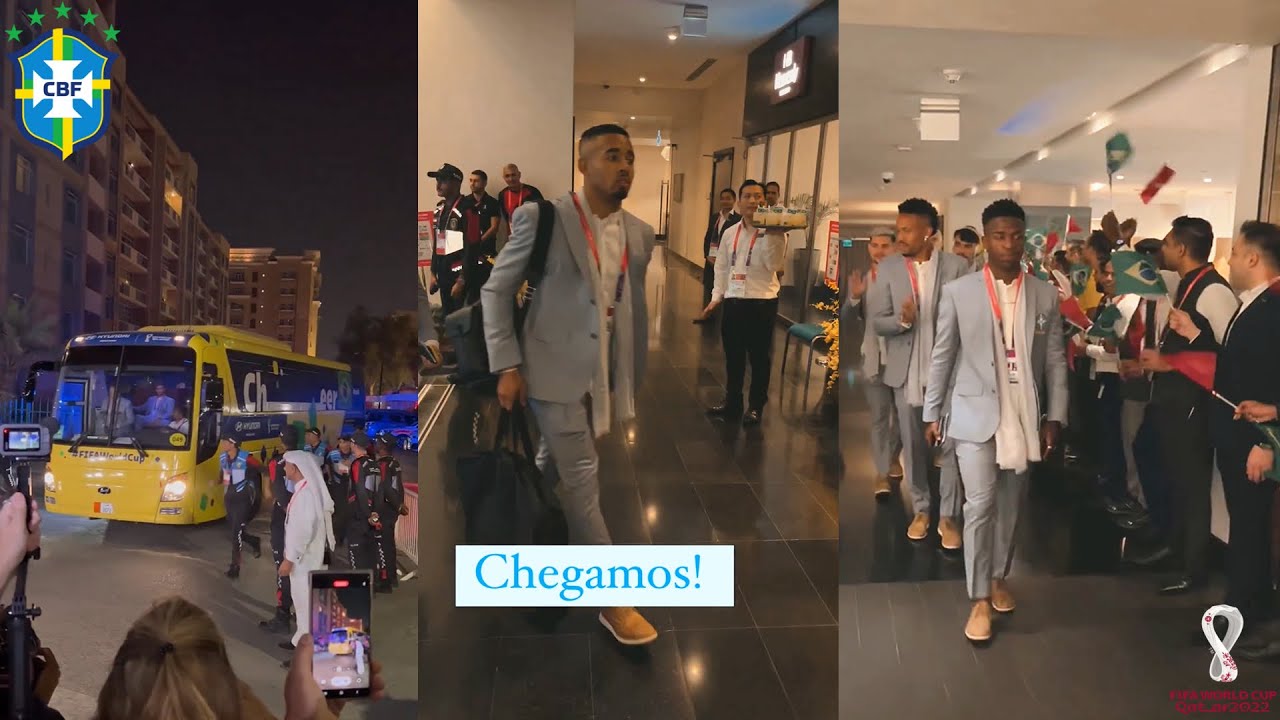 Brazil National Team Arrives in Qatar For The World Cup 202203 julho 2024
Brazil National Team Arrives in Qatar For The World Cup 202203 julho 2024 -
 Underfell Sans - M.RArts - Crafts & Other Art, Other Crafts & Art - ArtPal03 julho 2024
Underfell Sans - M.RArts - Crafts & Other Art, Other Crafts & Art - ArtPal03 julho 2024 -
 Garigari-kun × Pokémon Card Game Zarude V Promo Revealed, PokeGuardian03 julho 2024
Garigari-kun × Pokémon Card Game Zarude V Promo Revealed, PokeGuardian03 julho 2024 -
![23 CÓDIGOS] 🐯🍩 ¡NUEVOS CÓDIGOS DE NAVIDAD EN BLOX FRUITS ROBLOX](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/fsXS-yU5Ifk/maxresdefault.jpg) 23 CÓDIGOS] 🐯🍩 ¡NUEVOS CÓDIGOS DE NAVIDAD EN BLOX FRUITS ROBLOX03 julho 2024
23 CÓDIGOS] 🐯🍩 ¡NUEVOS CÓDIGOS DE NAVIDAD EN BLOX FRUITS ROBLOX03 julho 2024 -
 Menhera-chan Comparison 4/20 - 11/21 by Ny4nKitto on DeviantArt03 julho 2024
Menhera-chan Comparison 4/20 - 11/21 by Ny4nKitto on DeviantArt03 julho 2024

