Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 16 julho 2024
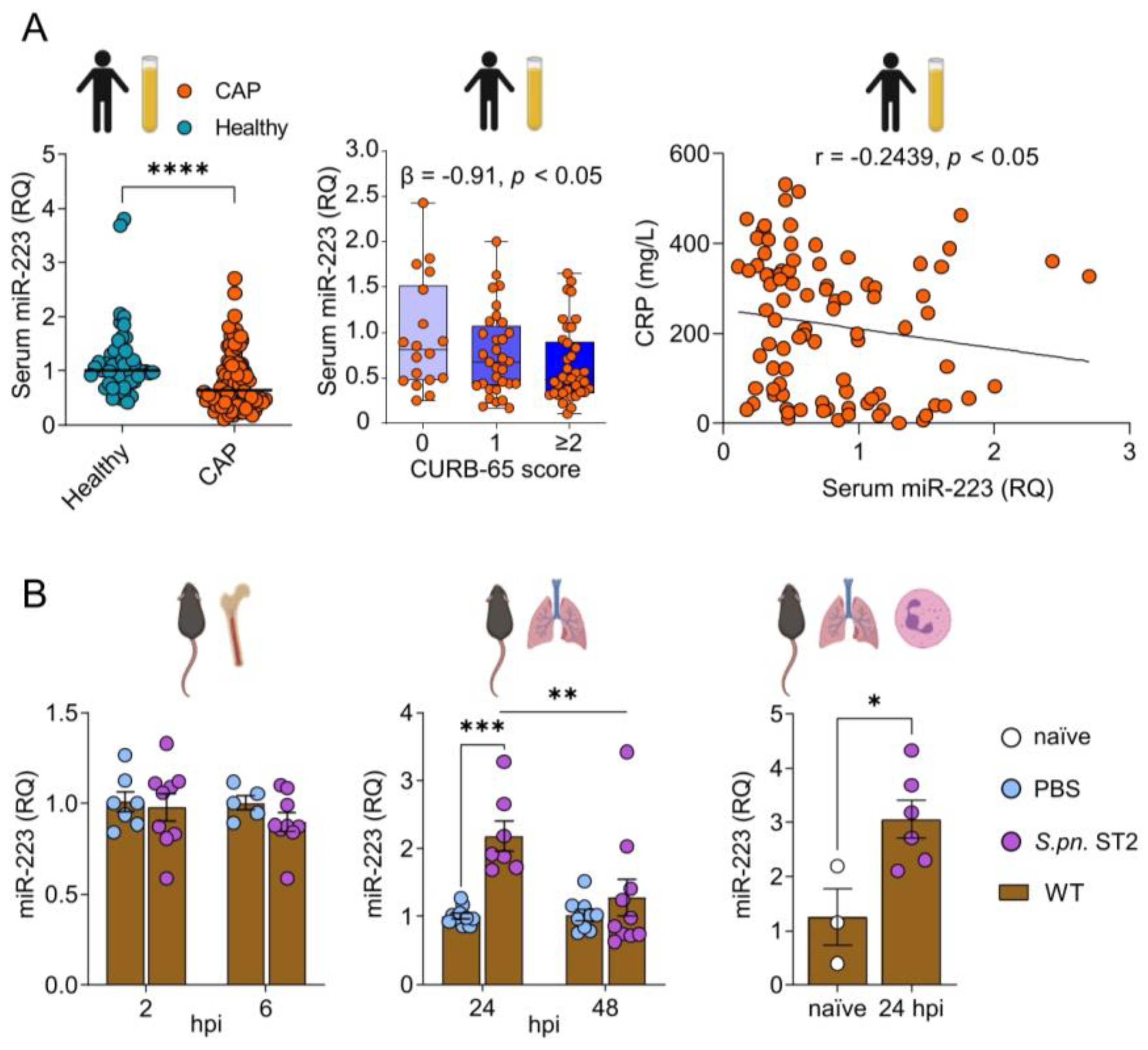
Community-acquired pneumonia remains a major contributor to global communicable disease-mediated mortality. Neutrophils play a leading role in trying to contain bacterial lung infection, but they also drive detrimental pulmonary inflammation, when dysregulated. Here we aimed at understanding the role of microRNA-223 in orchestrating pulmonary inflammation during pneumococcal pneumonia. Serum microRNA-223 was measured in patients with pneumococcal pneumonia and in healthy subjects. Pulmonary inflammation in wild-type and microRNA-223-knockout mice was assessed in terms of disease course, histopathology, cellular recruitment and evaluation of inflammatory protein and gene signatures following pneumococcal infection. Low levels of serum microRNA-223 correlated with increased disease severity in pneumococcal pneumonia patients. Prolonged neutrophilic influx into the lungs and alveolar spaces was detected in pneumococci-infected microRNA-223-knockout mice, possibly accounting for aggravated histopathology and acute lung injury. Expression of microRNA-223 in wild-type mice was induced by pneumococcal infection in a time-dependent manner in whole lungs and lung neutrophils. Single-cell transcriptome analyses of murine lungs revealed a unique profile of antimicrobial and cellular maturation genes that are dysregulated in neutrophils lacking microRNA-223. Taken together, low levels of microRNA-223 in human pneumonia patient serum were associated with increased disease severity, whilst its absence provoked dysregulation of the neutrophil transcriptome in murine pneumococcal pneumonia.
Nt Novo Cella Get File - Colaboratory
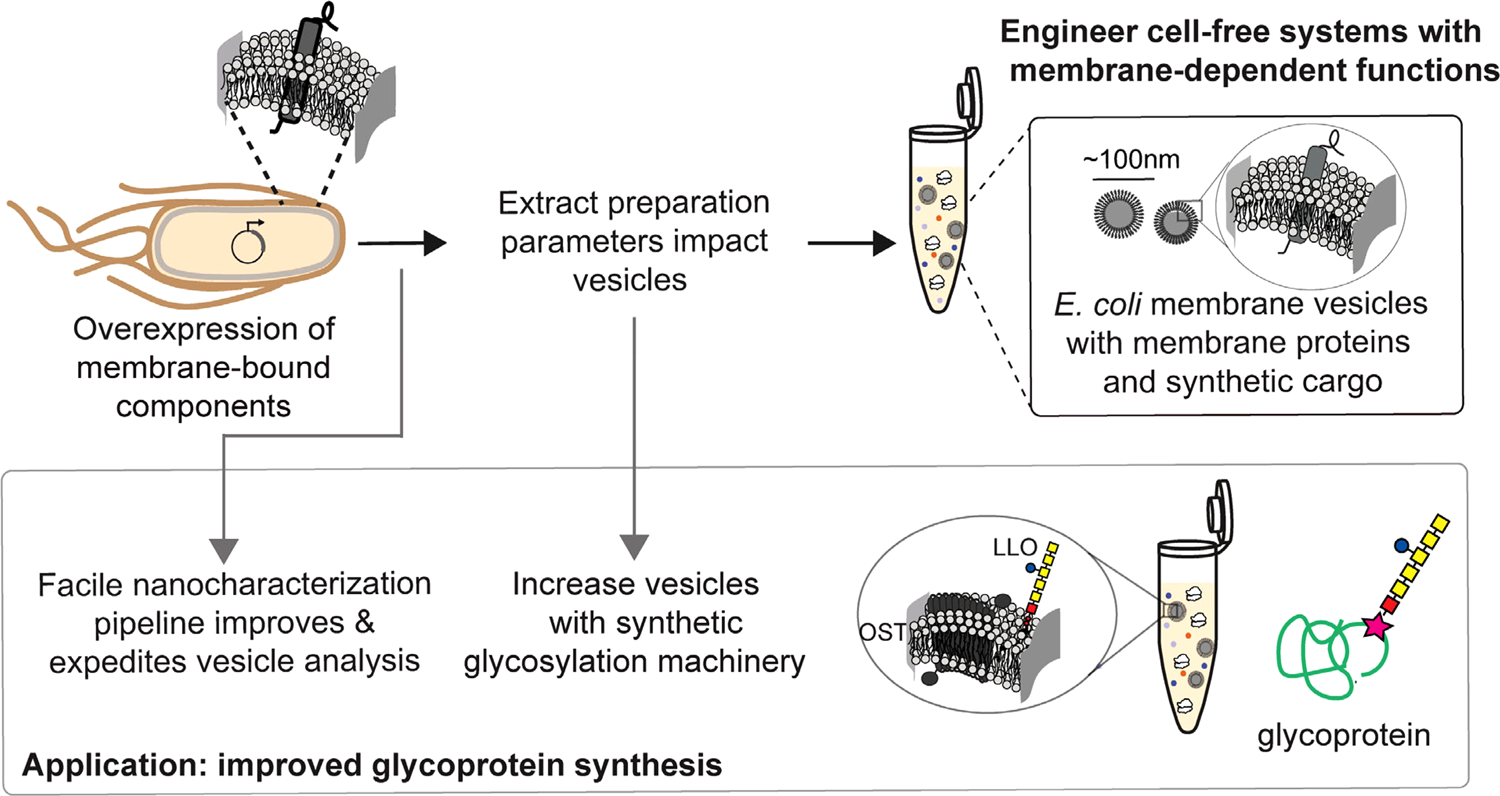
Improving cell-free glycoprotein synthesis by characterizing and enriching native membrane vesicles

Scheme of cell free cloning using DMF. ( A ) The full length construct
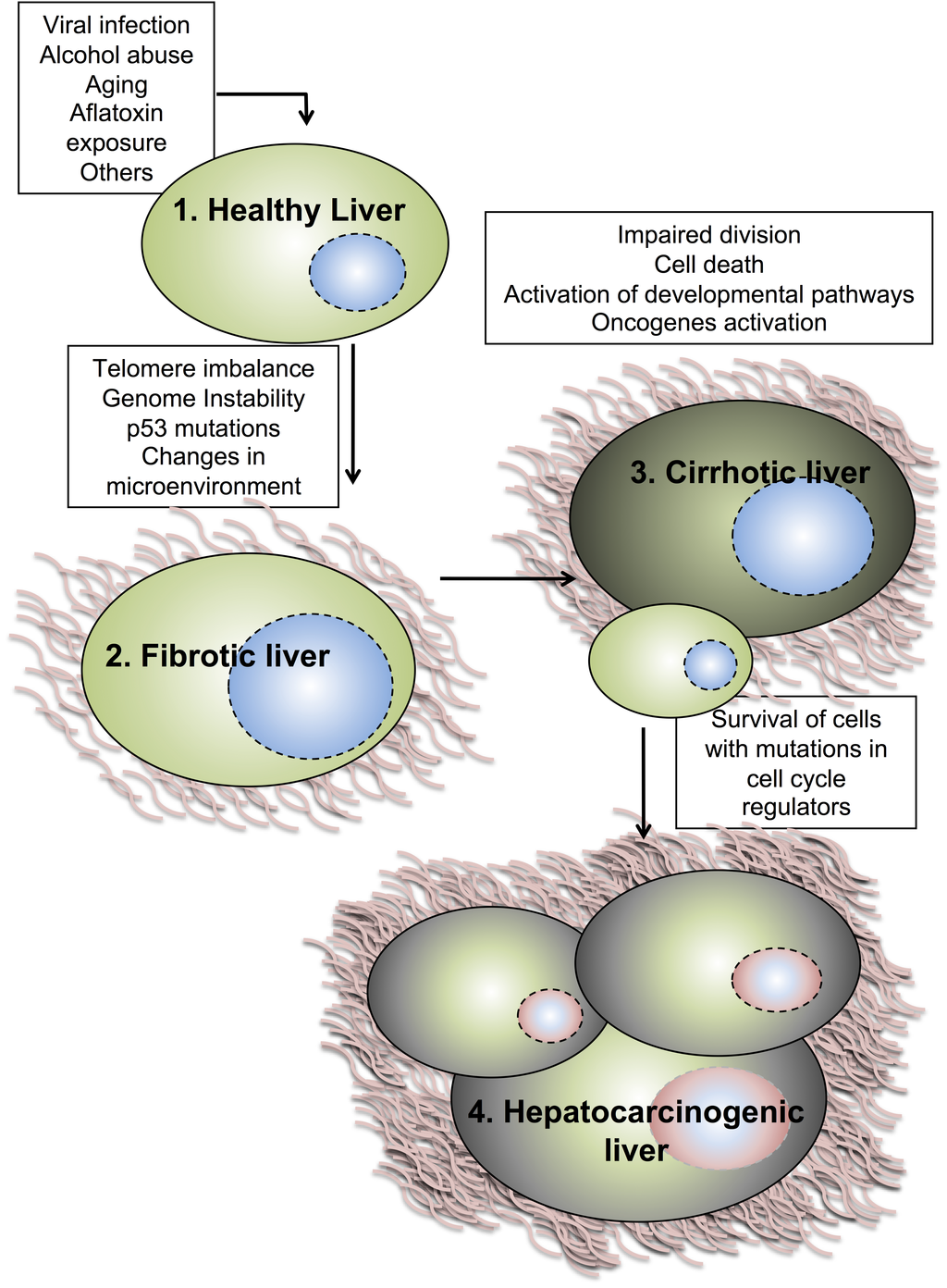
Cancers, Free Full-Text
Full-spectrum cell-free RAN for 6G systems: s
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology on X: From May cover Challenges and directions in studying cell–cell communication by #ExtracellularVesicles @DaveCarter1234 @guillaume_niel @VaderPieter Clayton Lambert & Raposo #EVsAreCool FREE pdf: https
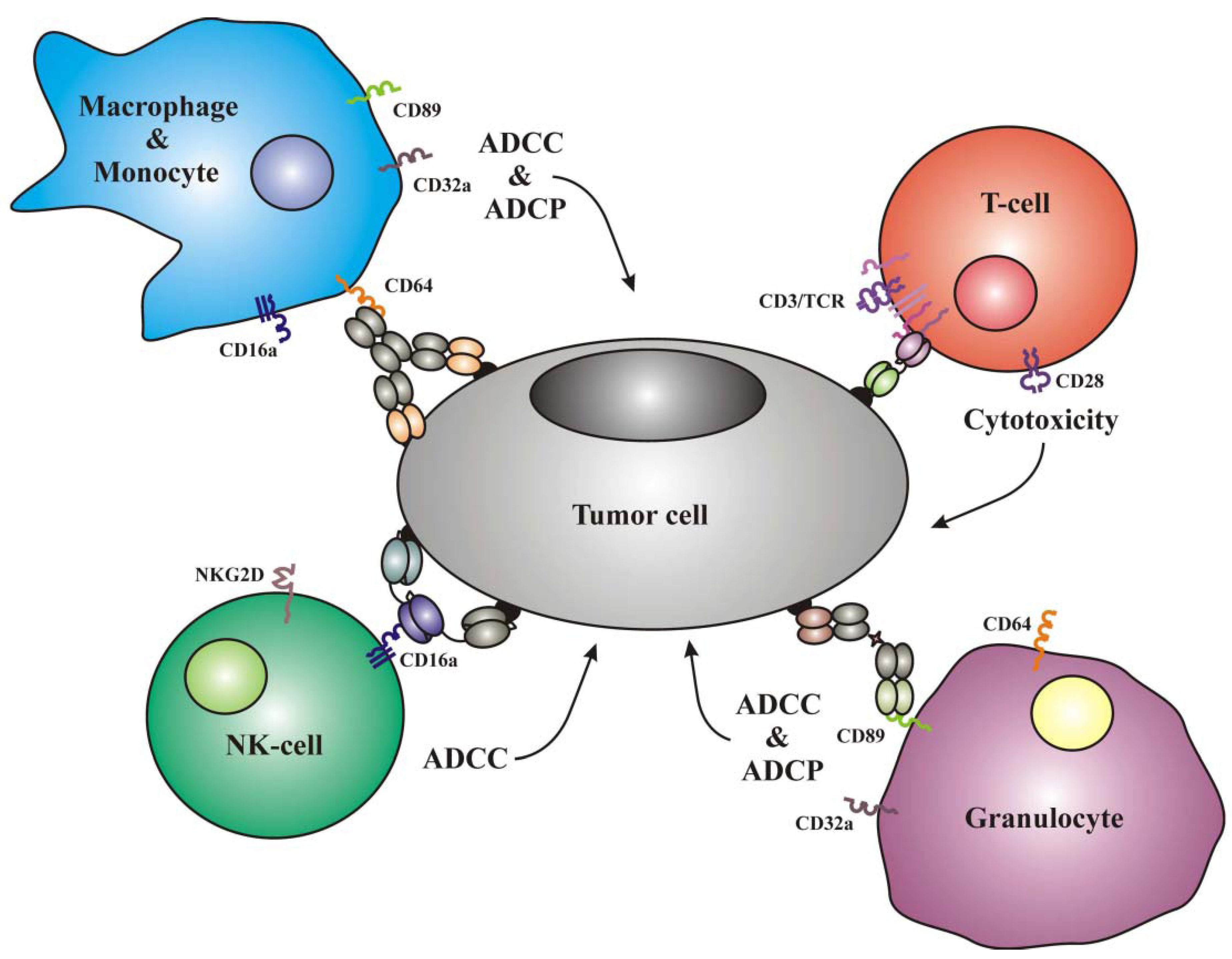
Antibodies, Free Full-Text

Sequencing of Circulating Cell-free DNA during Pregnancy
The dependence of cell-free protein synthesis in E. coli upon naturally occurring or synthetic polyribonucleotides. - Abstract - Europe PMC
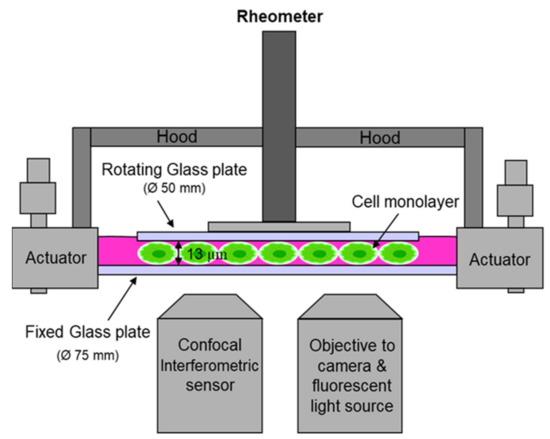
Ds Kumar Strömungsmechanik Pdf Kostenloser Download - Colaboratory
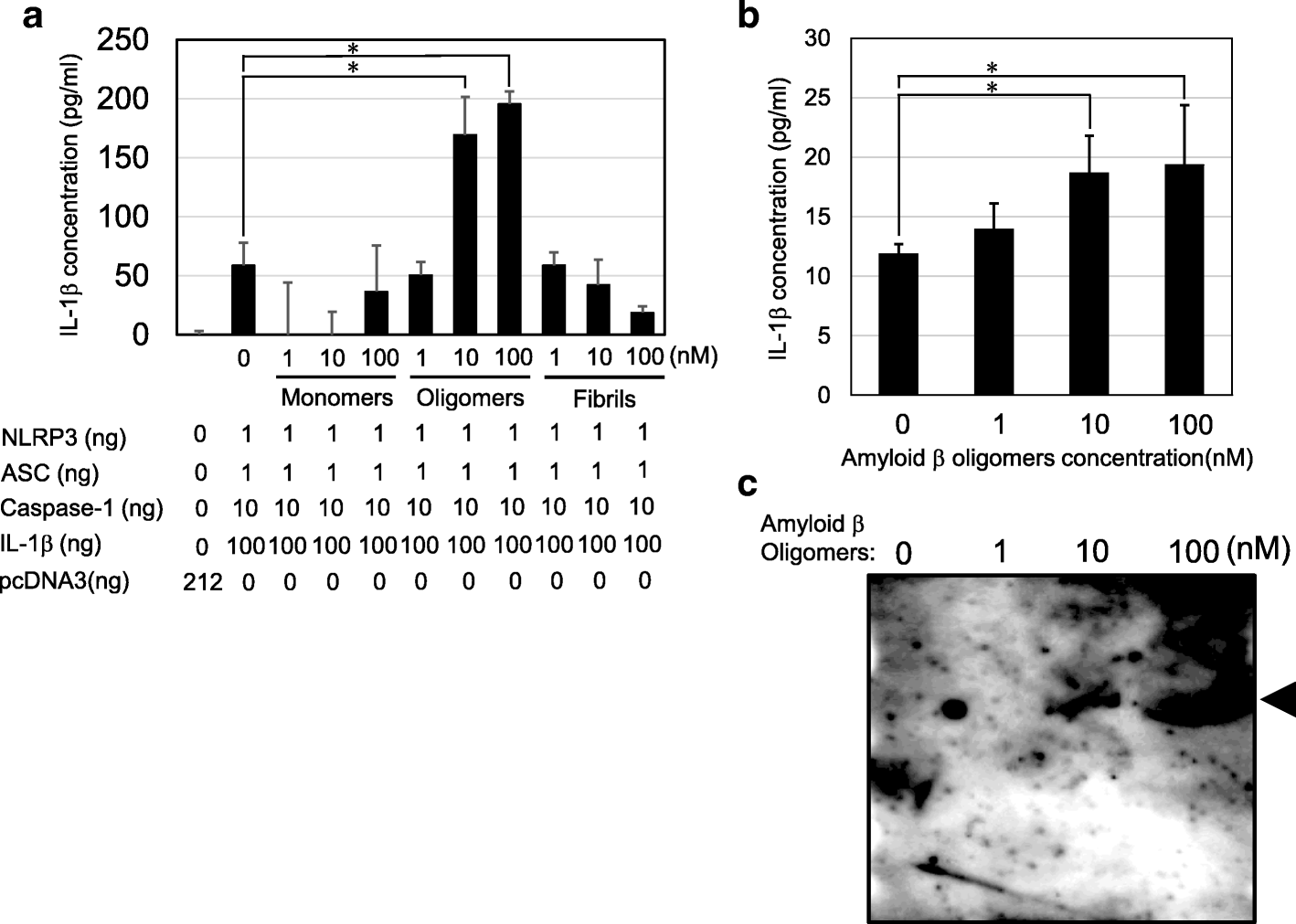
Amyloid β directly interacts with NLRP3 to initiate inflammasome activation: identification of an intrinsic NLRP3 ligand in a cell-free system, Inflammation and Regeneration
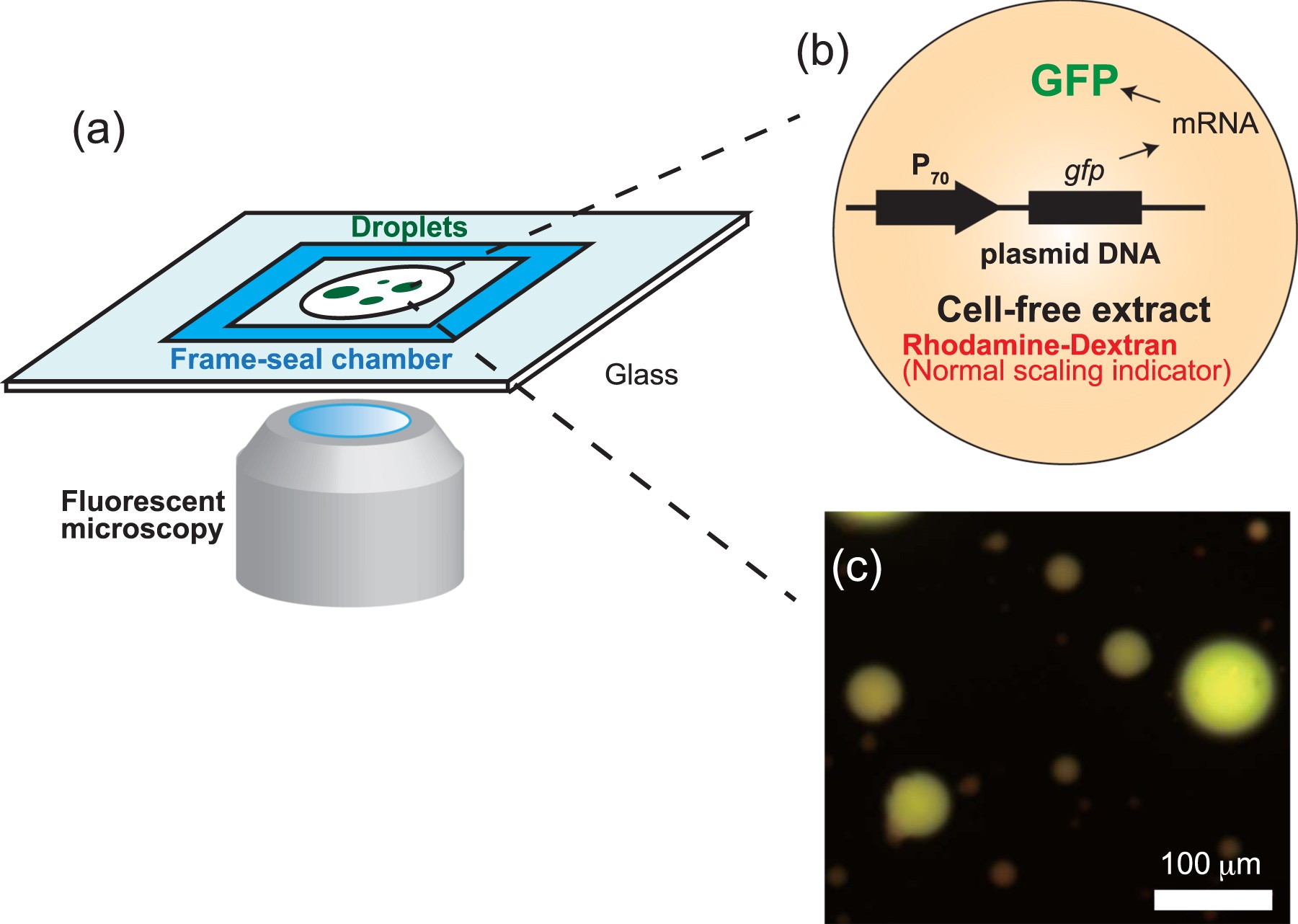
Anomalous Scaling of Gene Expression in Confined Cell-Free Reactions
Labile coat: reason for noninfectious cell-free varicella-zoster virus in culture. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Recomendado para você
-
 Apresentação Startup Show - Reality Empreendedorismo16 julho 2024
Apresentação Startup Show - Reality Empreendedorismo16 julho 2024 -
 AeC - App Robbyson - Realidade Aumentada16 julho 2024
AeC - App Robbyson - Realidade Aumentada16 julho 2024 -
 Robson AeC by Fernando Parreiras16 julho 2024
Robson AeC by Fernando Parreiras16 julho 2024 -
Robbyson Corporate by Robbyson - (Android Apps) — AppAgg16 julho 2024
-
 Premium Photo Asian boy dressed in dark blue with a light blue16 julho 2024
Premium Photo Asian boy dressed in dark blue with a light blue16 julho 2024 -
Robbyson Corporate Mobile APK (Android App) - Free Download16 julho 2024
-
 Case Job Caio Luna by Caio Nascimento16 julho 2024
Case Job Caio Luna by Caio Nascimento16 julho 2024 -
 Arquivos Robbyson - Portal ClienteSA16 julho 2024
Arquivos Robbyson - Portal ClienteSA16 julho 2024 -
Lawrence Klein no LinkedIn: #robbyson #conarec16 julho 2024
-
 Acompanhe o pedido Dunorte Distribuidora16 julho 2024
Acompanhe o pedido Dunorte Distribuidora16 julho 2024
você pode gostar
-
 How to find IP address in Kali Linux - Linux Tutorials - Learn Linux Configuration16 julho 2024
How to find IP address in Kali Linux - Linux Tutorials - Learn Linux Configuration16 julho 2024 -
 Figuarts Zero Chouette Pretty Guardian Sailor Moon Cosmos the Movie Eternal Sailor Moon -Darkness Calls to Light and Light Summons Darkness- - Tokyo Otaku Mode (TOM)16 julho 2024
Figuarts Zero Chouette Pretty Guardian Sailor Moon Cosmos the Movie Eternal Sailor Moon -Darkness Calls to Light and Light Summons Darkness- - Tokyo Otaku Mode (TOM)16 julho 2024 -
ACA NEOGEO THE KING OF FIGHTERS 2002 for Nintendo Switch - Nintendo Official Site16 julho 2024
-
 Pinball Hall of Fame: The Williams Collection Review (3DS)16 julho 2024
Pinball Hall of Fame: The Williams Collection Review (3DS)16 julho 2024 -
Anime: The Eminence in Shadow Season 2 _ Shadow Angry because Rose Ori16 julho 2024
-
Basic4. Practice Occupational Health and Safety Procedures, PDF, Occupational Safety And Health16 julho 2024
-
 Neo Geo Consolized MVS16 julho 2024
Neo Geo Consolized MVS16 julho 2024 -
 Project: Playtime on X: We're excited about the new content and updates we're adding to Project Playtime for Season 2, but unfortunately we had to temporarily remove the timer feature to make16 julho 2024
Project: Playtime on X: We're excited about the new content and updates we're adding to Project Playtime for Season 2, but unfortunately we had to temporarily remove the timer feature to make16 julho 2024 -
 How to sign up for a Hotmail Live Email address account16 julho 2024
How to sign up for a Hotmail Live Email address account16 julho 2024 -
 Desenho para colorir de sorvete Kawaii · Creative Fabrica16 julho 2024
Desenho para colorir de sorvete Kawaii · Creative Fabrica16 julho 2024



